Navigation Timing API
Definition
The Navigation Timing API is an endorsed W3C specification that defines a software-based interface that provides timing-related data for websites and applications that covers the complete user experience.
Endorsed in 2012 the original API specification has been widely adopted and available for use in browser technologies to provide a mechanism for performance metrics to be exposed for use by real-time analysis or historical data collection tools. The API provides 2 main interfaces
- PerformanceNavingation - this returns the last non-redirect navigation in the current browsing context.
- PerformanceTiming - this provides access to performance related attributes.
Both interfaces are presented in the illustration in the next section.
In 2019 a new specification, Navigation Timing 2, has been developed as a replacement for the original navigation timing API. The new version builds on the original 2012 scope and extends and builds on the existing timing interfaces and metrics while adding further performance-oriented data points. The replacement API is accessed using a new interface, PerformanceNavigationTiming, which supercedes the 2012 metrics.
In addition to the enhanced metrics, a major change between the versions is the way that time is measured. The 2012 specification measures all timing points in milliseconds since midnight of January 1, 1970 (UTC). Version 2 adopts the W3C High Resolution Time Level 2 recommendation that implements sub-millisecond granularity to timing points and measures all time values relative to the time origin of the Window object (this can be considered as the Document Object - DOM).
Version 2 also substantially enhances on the inherent security and privacy necessary to protect the data within the interface for example through limiting access to the interface and enforcement of the same-origin algorithm.
Usage
The diagram presents the attributes of the 2012 Navigation specification for both the PerformanceTiming and PerformanceNavigation interfaces.
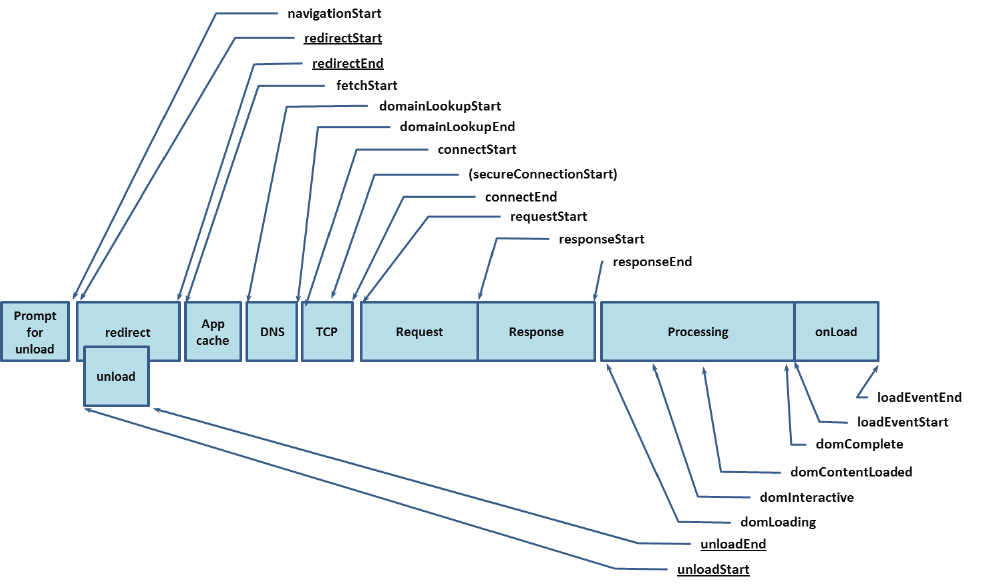
These interfaces are well established and available in almost every browser and should be available for some time but warnings are beginning to appear in colnsole logs that the timing points may be deprecated in future releases as version 2 becomes formalized and more widely adopted.
This illustration presents the version 2 timing attributes as defined by the PerformanceNavigationTiming interface.

There is considerable depth of detail available in the new interface and the specification details how to access the timing points and also defines the inter-relationships that exists between them. The new specification is already available in many browsers but it should not be assumed that the specification has been adopted. As expected it is older browsers, such as IE11 and Samsung UC, that do not have support but Safari and IOS may also be behind in adoptions. Verification of browser adoption can be checked using caniuse.com.
All interfaces are accessed using JavaScript but the Draft strongly advises that only the PerformanceNavigationTiming is now used for accessing performance data.
The wealth of timing and performance data available through these interfaces has enabled the development of comprehensive performance management systems such as APMs, RUM, synthetic monitoring and other performance monitoring tools.
Additional Information
Refer to the W3C specification Navigation Timing for more information on the original 2012 recommendation. The July 2019 version of the W3C draft specification Navigation Timing Level 2 provides more information on the new release that is under final review.
